3D Druck Prototypen: Eine Zukunftstechnologie fasst Fuß
3D Drucker und 3D Druck Prototypen stellen zunehmend ein immer bedeutsameres Thema dar. Kein Wunder, denn auch im realen Leben fasst diese revolutionäre Technologie zunehmend Fuß.
Das 3D Druck Verfahren wird auch additive Fertigung genannt. Denn bei der Herstellung von 3D Druck Prototypen werden selbst komplexe und dreidimensionale Gegenstände durch das sukzessive Hinzufügen weiterer Schichten hergestellt.
3D Druck Prototypen: Die generative Fertigung
Das 3D Druck Prototyping ist daher auch unter den Begriffen generative Fertigung oder Rapid-Technologien bekannt. Dabei sind die Anwendungsgebiete schier unerschöpflich und reichen vom Betriebsmittelbau und der Automatisierungstechnik in der Industrie über den medizinischen Sektor, den Modellbau und das Kunsthandwerk bis hin zum Rapid Prototyping 3D Druck in der Architektur oder bei der Produktion von Brillen.
Tatsächlich lassen sich in Form von 3D Druck Prototypen Fertigungsverfahren und auch die Markteinführung neuer Produkte drastisch verkürzen. Solche additiven Fertigungsverfahren werden bereits seit den 1980er Jahren eingesetzt. Dabei griff die generative Fertigung zur Herstellung von 3D Druck Prototypen auch auf bereits bekannte Verfahren wie den Siebdruck zurück.
Soweit die historische Betrachtung additiver Fertigung. Im Folgenden wollen wir einen näheren Blick auf neue 3D Drucker, moderne 3D Druck Prototypen und vor allem auch auf das dazu benötigte Ausgangsmaterial werfen.
3D Druck Prototypen: Eine neue Welt entsteht!
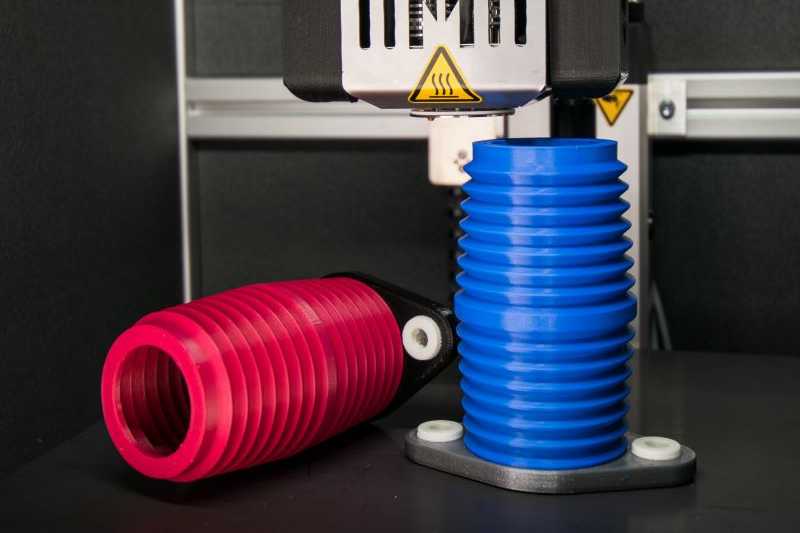
Tatsächlich kommt es nämlich nicht nur auf den Drucker, sondern auch auf das sogenannte Filament an. Dieses stellt mithin die Basis, respektive das Ausgangsmaterial, für einen jeden 3D Druck Prototypen dar.
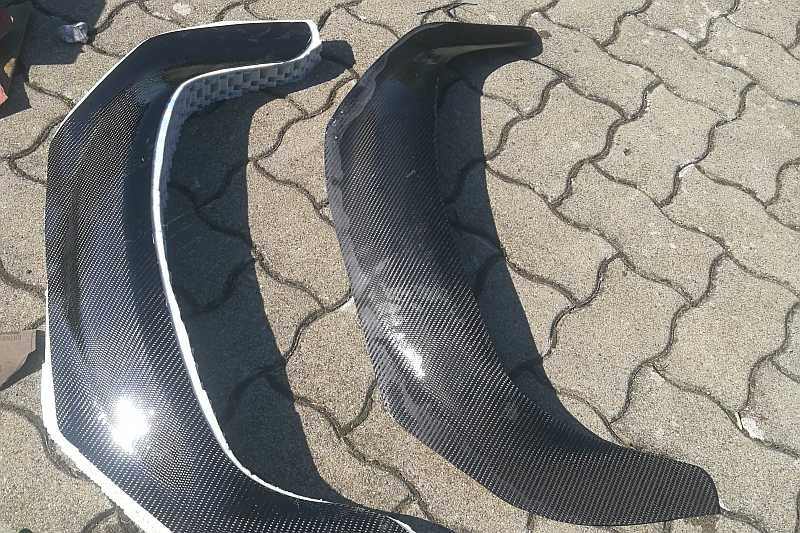
Das 3D-Druck-Filament, aus dem dann später die 3D Druck Prototypen entstehen, ist auf Rollen gewickelt und wird während des Druckvorgangs im Drucker erhitzt. Dabei gibt es viele unterschiedliche Filament-Arten. Die Wahl ob des richtigen Materials hängt dabei nicht zuletzt vom zu fertigenden Produkt, dem 3D Druck Prototypen, ab. Unter anderem gibt es im Bereich der Fertigung von 3D Druck Prototypen Kunststoffe wie PLA, aber auch CarbonFilament, welches von vielen professionellen Firmen eingesetzt wird. Zu bedenken ist beim Carbon-Filament freilich, dass bei Einsatz dieses Materials gehärtete Düsen eingesetzt werden sollten. Normale Messingdüsen verschleißen aufgrund der abrasiven Eigenschaft der Kohlefasern sehr schnell.
Filamente - die Basis eines jeden 3D Druck Prototypen
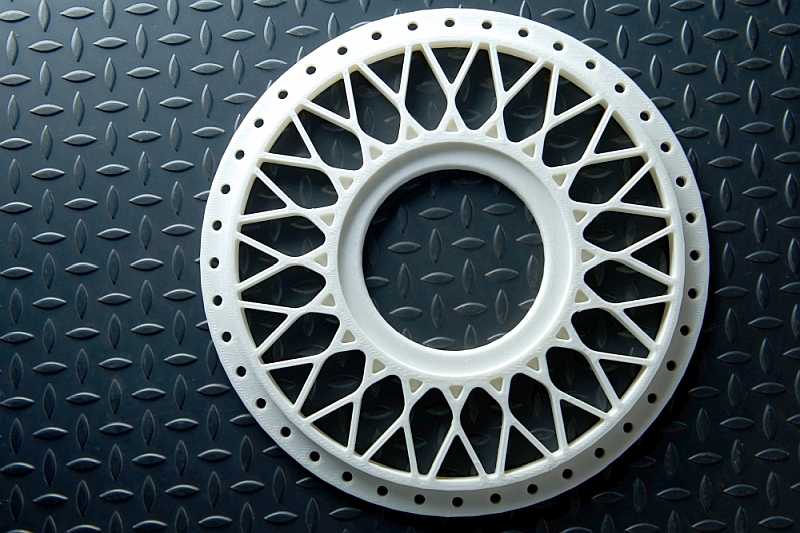
Es gibt verschiedene Filamente auf dem Markt. Für den industriellen Einsatz sind dabei Filamente mit besonderen Eigenschaften, wie einer elektrischen Leitfähigkeit (ESD-fähige Filamente) oder schwer entflammbare Filamente von größter Relevanz. Es gibt aber auch so genanntes leuchtendes Filament, das ganz besondere 3D Druck Prototypen möglich macht.
Sämtliche Filamente zur Produktion von 3D Druck Prototypen haben somit ihr Für und Wider. Natürlich auch im Hinblick darauf, wo und wie die fertigen Produkte im Nachhinein eingesetzt werden. Zudem kommen natürlich ständig neue Produkte und Ideen im Rahmen der 3D Druck Prototypen Fertigung auf den Markt.
Wir von der Firma Multec setzen gerne PLA HT als ABS-Ersatz ein. Denn dabei werden bei der Fertigung von 3 D Druck Prototypen viele der Nachteile von ABS eliminiert. So zeichnet sich das erhältliche Hochleistungs-PLA-Filament von Multec durch zahlreiche interessante Eigenschaften aus. Es ist überaus robust, äußerst temperaturbeständig und bürgt für eine exzellente Druckbarkeit.
3D Prototypen: Fazit
Wenn wir ein Fazit in Sachen 3D Druck Prototypen wagen wollen, bleibt festzuhalten, dass uns heute eine Technologie zur Verfügung steht, die noch vor einigen Jahrzehnten einer Utopie gleichkam. Längst scheinen Gelenke aus dem 3D Drucker möglich und auch für die Zahnmedizin mutiert diese Verfahren zu einem absoluten Gamechanger.
Bei weiteren Fragen zum Thema 3D Prototypen dürfen Sie gerne jederzeit Kontakt zu uns aufnehmen! Wir freuen uns auf Ihre Nachricht.